The Age of Enlightenment
The Age of Enlightenment was a period when reason and rationality propelled humanity forward. Its thinkers were instrumental in shaping American Revolution, leading to the creation of a new nation. From John Locke’s ideas on natural rights to Montesquieu’s theories about separation of powers, the influence is undeniable. The Founding Fathers were deeply entrenched in Enlightenment ideology, which helped them lay down the foundation for modern democracy. With their support, American Revolution became more than just a battle for freedom; it was a movement that ultimately changed the world.
Enlightenment ideals had key implications for society and politics, most notably individual liberties such as freedom of speech and religion. Moreover, its principles like equality before law, popular sovereignty and liberty of conscience reflect in the United States Constitution (1787). These concepts also inspired influential figures such as Benjamin Franklin and Thomas Paine who advocated for human rights activism.
From understanding how power should be divided to recognizing citizens’ right to challenge authority – Enlightenment philosophers made significant contributions to American Revolution and beyond. Their philosophical musings not only helped shape our world but also inspired ideas that promoted social justice and democratic values.
With patriots fighting tooth and nail against British tyranny, it is hard to imagine what might have happened if Enlightenment Thinkers had not influenced the Founding Fathers. Today, we stand at the intersection of history and progress where America continues to embody Enlightened principles in its political foundation. Embrace these principles now to drive change for a brighter future!
Who knew a bunch of old dead guys with funny names could have such a big impact on America?
Key Enlightenment Thinkers
To gain a deeper understanding of the key enlightenment thinkers who influenced the founding fathers during the American Revolution, it’s essential to explore their individual philosophies. Hence, John Locke’s philosophy and influence on founding fathers, Montesquieu’s philosophy and influence on founding fathers, Voltaire’s philosophy and influence on founding fathers, and Rousseau’s philosophy and influence on founding fathers will be discussed in this section.
John Locke – His Philosophy and influence on Founding Fathers
John Locke’s ideology inspired the founding fathers to pursue independence from Great Britain. He believed that every individual had a natural right to life, liberty, and property, and that governments exist primarily to secure these rights. The Declaration of Independence heavily drew on his ideas to establish the foundations of American democracy.

Locke was an influential Enlightenment philosopher who rejected the idea of divine right monarchy and social hierarchy. His advocacy for religious tolerance and separation of church and state challenged traditional notions of political authority. Through his emphasis on the importance of reason, knowledge, and individual autonomy, he brought about a new era of philosophical thought.
It is interesting to note that Locke’s libertarian views found resonance among some prominent 20th-century thinkers, such as Ayn Rand and Robert Nozick. His enduring legacy continues to play a vital role in contemporary debates on human rights, constitutional law, and civic engagement.
Pro tip: To understand John Locke’s philosophy better, read his seminal work ‘Two Treatises of Government.’
Montesquieu’s ideas may have influenced the Founding Fathers, but let’s not forget that he also inspired Napoleon, so maybe take his philosophy with a grain of salt.
Montesquieu – His Philosophy and influence on Founding Fathers
Montesquieu’s Philosophical Ideas and Impact on Founding Fathers is a crucial area of study. Montesquieu explored the concept of separation of powers and the importance of checks and balances in government. This inspired the Founding Fathers, who integrated Montesquieu’s ideas into the United States Constitution.

The French philosopher Charles-Louis de Secondat, known as Montesquieu, was a significant contributor to political theory. He believed that separating powers among executive, legislative and judiciary branches helped ensure balanced governance. Furthermore, he emphasized the significance of checks and balances to prevent corruption in government. The Founding Fathers appreciated his ideologies and were influenced while drafting the constitution.
In addition to founding fathers’ influence on the constitution, Montesquieu contributed to modern democracy’s progress profoundly. He argued for a constitutional monarchy that restricted its power through laws and governing principles. Consequently, this laid a foundation for future liberal ideas reflecting democratic values.
In today’s world where democracy faces diverse challenges globally, Montesquieu’s ideas remain relevant in promoting freedom of speech and human rights protection. His philosophy teaches us that combining cooperation with compliance ensures successful governance systems that benefit society overall.
Voltaire may have been one of the Founding Fathers’ favorite philosophers, but I bet they never let him participate in their political debates.
Voltaire – His Philosophy and influence on Founding Fathers
Voltaire’s thoughts on freedom, individualism and equality had a tremendous impact on the Founding Fathers of America. His philosophical ideology was rooted in rationalism, skepticism and empiricism which challenged the mainstream Catholic beliefs of his time. These ideals were reflected in his various works ranging from political treatises to plays.
The influence of Voltaire’s ideas can be seen evident in the American Declaration of Independence through the concept of “life, liberty and the pursuit of happiness. He firmly advocated for religious tolerance, separation of powers, constitutional monarchy and civil rights. The Founding Fathers admired him as he propagated these same ideas for a democratic society.
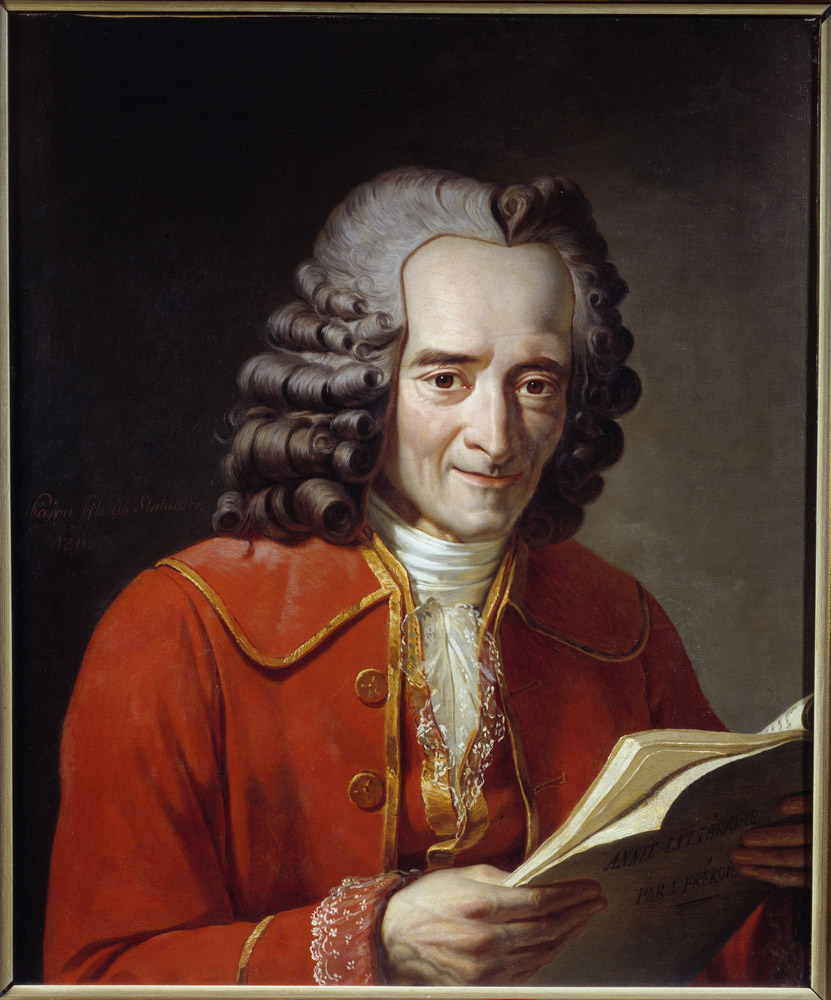

Interestingly, Voltaire exchanged letters with Thomas Jefferson discussing their beliefs on the principles inherent to commerce; however, they both held differing opinions on religion.
A true fact about Voltaire is that alongside his contributions to philosophy and politics, he was also a famous writer and playwright with one of his most famous works being Candide.
He may have inspired some of the Founding Fathers, but I bet Rousseau never imagined a reality TV star could become president.
Rousseau – His Philosophy and influence on Founding Fathers
Rousseau’s Philosophy and Influence on the American Founders can be observed through his work in social contract theory, emphasizing the importance of natural liberties and individualism. This influence was particularly prominent in shaping the Declaration of Independence and the US Constitution.

Rousseau’s emphasis on direct democracy, which prioritized citizens’ voice in decision-making, strongly impacted American political philosophy. His advocacy for government institutions that had a spirit of collaboration and equality rather than power-driven hierarchies also influenced the structures of America’s governing system.
It is worth noting that there were mixed reviews about Rousseau among American founders. This included Thomas Jefferson who saw him as an influential thinker, while John Adams viewed him as a fanatic. Nonetheless, Rousseau still played a significant role in shaping America’s view of liberty and individual rights.
According to historians, Benjamin Franklin had a pleasant encounter with Jean-Jacques Rousseau in France when he was serving as an ambassador to France. Franklin used this opportunity to invite Rousseau to visit the colonies alongside Voltaire, who also declined admittance into both countries due to vast disagreements with their leaders.
If only the Founding Fathers had been a bit more enlightened about slavery, we might not be dealing with its legacy today.
Founding Fathers and their views on Enlightenment Philosophy
To understand the Founding Fathers and their views on Enlightenment Philosophy in the American Revolution, explore the sub-sections on Thomas Jefferson’s affinity towards Enlightenment Philosophy, Benjamin Franklin’s role in promoting Enlightenment Philosophy, and George Washington’s views on Enlightenment Philosophy.
Thomas Jefferson – His affinity towards Enlightenment Philosophy
Thomas Jefferson, one of America’s Founding Fathers, had a profound connection to Enlightenment Philosophy. His intellectual curiosity and belief in individual freedom were inspired by the writings of philosophers like John Locke and Jean-Jacques Rousseau. Jefferson’s political ideals were heavily influenced by this philosophical movement, as he believed in natural rights, democracy, scientific inquiry, and reason.
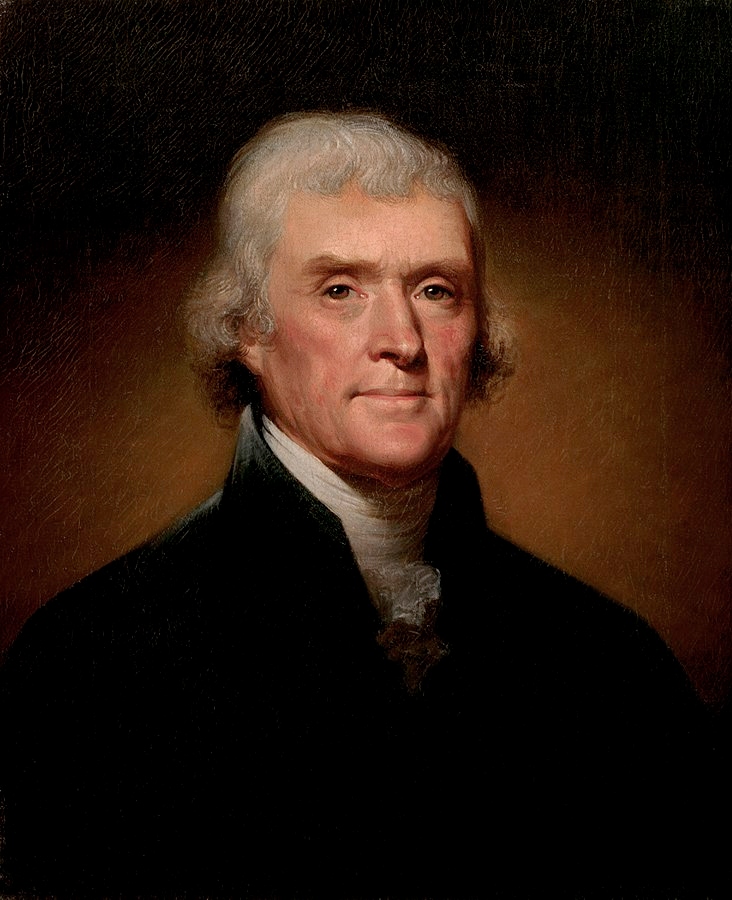

Jefferson’s affinity towards Enlightenment Philosophy is evident from his contributions to American institutions such as the Declaration of Independence and the Virginia Statute for Religious Freedom. He advocated for religious tolerance and criticized any form of authoritarianism that could restrict individual liberty. Additionally, Jefferson was a strong proponent of free speech and press, attesting that the rights to these crucial concepts are vital for democratic societies.
Furthermore, Jefferson corresponded with various Enlightenment thinkers such as Benjamin Franklin, Voltaire, and Adam Smith. These correspondences depict his deep interest in philosophy as well as expressing himself adequately in writing.
Pro Tip: To gain an insightful understanding of the Founding Fathers’ perspectives, it is imperative to study their philosophical influences on American politics closely.
Benjamin Franklin was the ultimate hype man for Enlightenment Philosophy, spreading it like wildfire and making it cooler than a polar bear’s toenails.
Benjamin Franklin – His role in promoting Enlightenment Philosophy
Benjamin Franklin was a prominent member of the Founding Fathers who contributed immensely to promoting Enlightenment Philosophy. His sharp intellect and wit allowed him to convey complex philosophical ideas in simple terms, making him a popular figure amongst fellow Enlightenment thinkers. Franklin’s views on science, education, and practicality were informed by his adherence to Enlightenment Philosophy. He championed reason and advocated for rational thought processes while also adapting new ideas with an open mind.
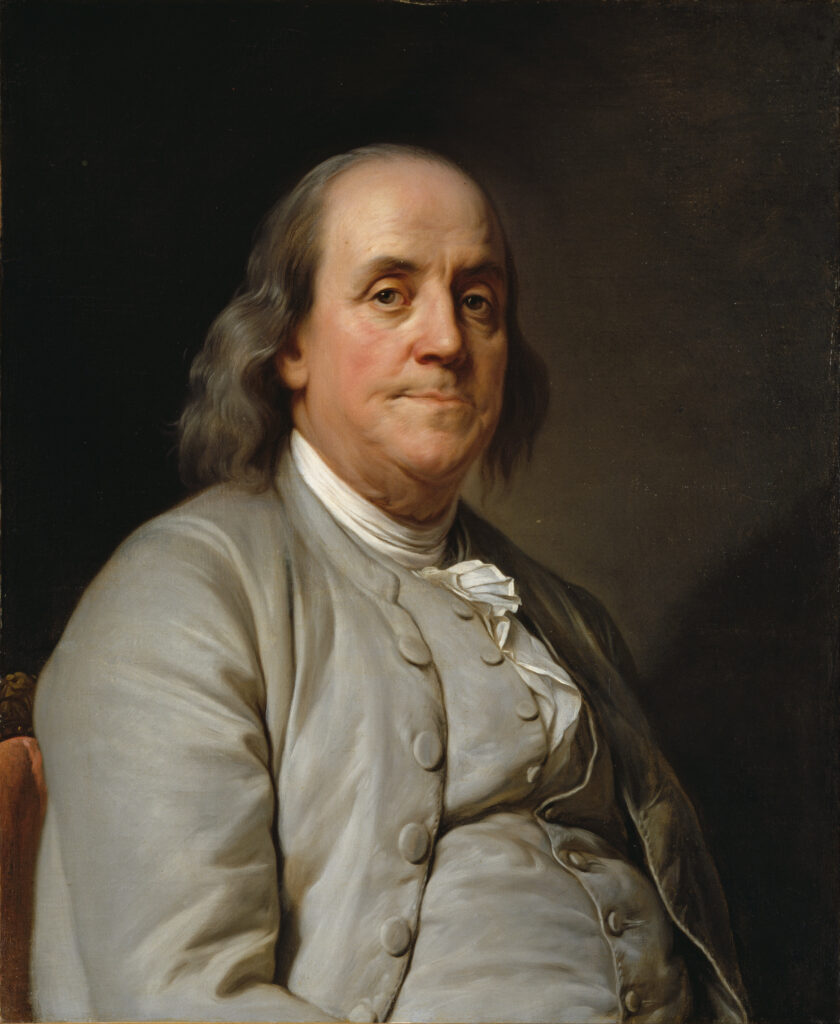

Franklin’s contributions were not limited to just theory — he put his beliefs into practice by establishing educational institutions like the University of Pennsylvania. He also conducted experiments that helped pave the way for revolutionary inventions in the fields of electricity and physics. His diplomatic skills played a crucial role in the successful formation of the United States, as he used reason and persuasion to bring people together.
It is notable that Benjamin Franklin was not alone in his advocacy for Enlightenment Philosophy amongst the Founding Fathers. Other influential figures like Thomas Jefferson and James Madison shared his views and strove towards ensuring that such principles became integral parts of American society.
In fact, Enlightenment Philosophy played a fundamental role in shaping many aspects of modern Western civilization. It sparked intellectual curiosity and led to significant advancements across various fields, including science, politics, art, and literature. Today, it continues to influence our lives through its emphasis on critical thinking and individual rights — two core tenets that formed the basis of America’s inception.
George Washington may have chopped down a cherry tree, but he definitely didn’t cut corners when it came to embracing Enlightenment Philosophy.
George Washington – His views on Enlightenment Philosophy
As a prominent founding father, George Washington had a nuanced understanding of Enlightenment Philosophy that colored his views. His personal beliefs centered on the importance of reason, learning and critical thinking in shaping both individuals and societies. Specifically, he believed that education served as a cornerstone for individual freedom and emphasized the need for all people to have access to education.

Washington also believed that enlightened leaders were necessary for creating governance structures that were responsive to the needs of their communities. He found inspiration in philosophers such as John Locke, whose ideas formed the basis for modern democracy. Unique details about Washington’s views on Enlightenment Philosophy include his advocacy for religious tolerance as well as his emphasis on scientific progress as an essential element of societal advancement. These beliefs helped shape the democratic ideals central to American politics today.
To further incorporate Washington’s philosophy into our daily lives, it is important to pay attention to educational equity while promoting critical thinking skills. By ensuring access to quality education for all, we can cultivate responsible citizens who contribute positively to our communities. Additionally, supporting scientific research and inquiry can help us remain at the forefront of societal progress, just as Washington envisioned.
The Founding Fathers were so enlightened, they could’ve lit up the entire American Revolution with their ideas.
Impact of Enlightenment Thinkers on American Revolution
To better understand how Enlightenment thinkers had an impact on the American Revolution, you can examine the three sub-sections: Influence on the Declaration of Independence, Influence on the American Constitution, and Role in the American Revolution. Each sub-section sheds light on how Enlightenment philosophers influenced the founding fathers of America and how these ideas were woven into the fabric of the nation’s founding documents and events.
Influence on the Declaration of Independence
The thoughts of Enlightenment thinkers strongly influenced the wording and spirit of the Declaration of Independence. The concept of natural rights, put forth by philosophers like John Locke, is reflected in the famous words penned by Thomas Jefferson: “We hold these truths to be self-evident, that all men are created equal, that they are endowed by their Creator with certain unalienable Rights, that among these are Life, Liberty and the pursuit of Happiness.” The document also drew on Montesquieu’s ideas about separation of powers and checks and balances to limit government power.

The impact of Enlightenment thinkers on the Declaration of Independence was significant in shaping its core principles. It rejected monarchy, embraced democracy, and championed individualism. These ideas were revolutionary for their time and continue to shape modern political thought.
It is important to note that while the Declaration drew upon Enlightenment thinkers’ concepts, it did not blindly follow them. For example, some philosophers believed in a social contract between citizens and government which could justify rebellion; however, Jefferson preferred a more moderate approach and argued for rebellion only as a last resort.
The history revealed how powerful ideas can change history; from the development of personal liberties to progressive movements around civil rights.
The Enlightenment Thinkers were to the American Constitution what seasoning is to a dish – they added the necessary flavor to make it palatable.
Influence on the American Constitution
The thinking of Enlightenment philosophers greatly influenced the American Constitution. Their beliefs in individual freedom, natural rights, and the social contract are evident in some of the most significant documents in American history. The founders of America took from Enlightenment concepts such as limited government and a separation of powers, which laid down the foundation of democracy. These ideas have become so synonymous with contemporary America that imagining a country without them seems impossible.
The authors of the Constitution, inspired by Enlightenment thinkers like John Locke and Montesquieu advocated for the right to property, religious freedom, equal representation under law, and self-government. Even though their philosophies had a historical context that was different from their application today; they created a framework for governance founded on principles that have given humans an ethical means for coexisting peacefully for centuries.

These thoughts impacted not only the Constitution but also many aspects of life around us today. They were prevalent from challenging authority to enabling progressive society views’ advancement throughout US History.
As we move toward an ever-evolving world surrounded by digital technologies and innovations – its power is uncontrollable – recall the influence our classics imparted on us historically. By drawing inspiration from our past generations, we can gain insight into modern times’ complex challenges and help solve them brilliantly according to luminaries like Benjamin Franklin – making every effort to create good institutions!
Enlightenment thinkers weren’t just blowing smoke when they talked about liberty and equality – their ideas helped light the fuse of the American Revolution.
Role in the American Revolution
The impact of Enlightenment thinkers during the American Revolution was significant. Their ideas helped shape the philosophical and political views of the colonists, paving the way for a movement towards independence and democracy. The concept of natural rights as articulated by Locke resonated with many colonists who believed it was their right to be represented in government. Similarly, Montesquieu’s separation of powers influenced the creation of the United States Constitution, further solidifying the ideals of democracy.
These Enlightenment thinkers played not only a role in shaping the ideology behind the American Revolution but also provided practical support. Benjamin Franklin used his position as an ambassador to France to secure essential French aid for revolutionary forces, ultimately leading to victory. Thomas Paine’s writings, especially ‘Common Sense’, galvanized public opinion against British rule.
While often overlooked in history books, women were instrumental in supporting revolutionary ideals. Many were inspired by Enlightenment values and actively participated in boycotts and protests against British rule. Their efforts led to better opportunities for women in education and increased involvement in political life.
John Adams once wrote that without Enlightenment thinkers, there may not have been an American Revolution at all. Despite their importance, their contributions are often understated or forgotten. It is crucial to recognize their impact on history and how their ideas continue to influence democratic nations worldwide today. Enlightenment thinkers may be long gone, but their impact on modern America can be felt like a shock from a well-grounded lightning rod.
Legacy of Enlightenment Philosophy in modern America
Enlightenment Philosophy was a critical influence on the Founding Fathers’ ideas and actions during the American Revolution. Its legacy still resonates in modern America, shaping political discourse and social progress. The principles of rationality, individual rights, separation of powers, and freedom of speech are all rooted in Enlightenment Philosophy.
The ideas of philosophers such as John Locke, Voltaire, and Jean-Jacques Rousseau inspired the Founding Fathers to challenge authoritarian rule and strive for democracy. The Declaration of Independence, with its emphasis on individual liberties and natural rights, reflects Enlightenment ideals.
In modern America, these same principles continue to shape society. For example, many initiatives aimed at promoting diversity and equality can be traced back to Enlightenment principles of tolerance and individual dignity. Furthermore, the influence of Enlightenment philosophers is evident in debates over issues such as free speech, gun control, and climate change.
To maintain this legacy going forward requires acknowledging its roots in history while embracing new perspectives that allow us to adapt it to our current challenges. One suggestion is to promote an inclusive approach that recognizes diverse voices and experiences while striving for a common understanding of how best to achieve societal goals. Another is to continue championing education as a means of promoting informed citizens who can engage critically with complex issues facing modern society.
Conclusion
This analysis shows that the Founding Fathers’ mindset was heavily influenced by Enlightenment thinkers. Through their writings and debates, they espoused ideas of natural rights, social contracts, and limited government, which ultimately served as a blueprint for the American Revolution. Their ideas have continued to shape American society and politics. It is therefore important to recognize the significant role played by these philosophers in shaping modern Western thought.
Pro Tip: To further understand the influence of Enlightenment thinkers on the Founding Fathers, consider studying their works in depth.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Who were the Enlightenment Thinkers that influenced the Founding Fathers?
A: Some Enlightenment Thinkers that influenced the Founding Fathers were John Locke, Montesquieu, and Jean-Jacques Rousseau.
Q: How did Enlightenment ideas influence the Founding Fathers’ beliefs about government?
A: Enlightenment ideas influenced the Founding Fathers to believe in natural rights, social contracts, and the separation of powers in government.
Q: How did Enlightenment ideas influence the American Revolution?
A: Enlightenment ideas inspired colonists to question the authority of the British monarch and demand representation in government.
Q: What specific ideas from the Enlightenment were incorporated into the Declaration of Independence?
A: The Declaration of Independence incorporated ideas about natural rights, the social contract, and the right to revolution.
Q: Did all of the Founding Fathers agree with Enlightenment ideas?
A: Not all Founding Fathers agreed with Enlightenment ideas, but they were still influential in shaping the beliefs of those who did.
Q: How did Enlightenment ideas impact the drafting of the U.S. Constitution?
A: Enlightenment ideas influenced the drafting of the U.S. Constitution by inspiring the creation of a federal system of government, the Bill of Rights, and the separation of powers between different branches of government.